Profile
Hey! We are Sohyee & Sherlyn:D
Welcome to our physics blog!:D Hope that you will learn something new here! Enjoy your stay:) Tagboard
Get your chat box here, or here. Width : <250
Height : Anything you want.
Affiliates
Archives
Stalker
|
June 26, 2010 at 12:30 PM MASS Mass is the amount of matter present in a body. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg). Small masses may be measured in grams (g) and large ones in tonnes (1 tonne = 1000 kg). Mass is a property of a body that cannot be changed by its location, speed and shape. For example if your mass on Earth is 60kg, it will still be 60kg even if you were on Moon or floating weightlessly in outer space. All bodies with mass possess a property known as inertia. The inertia of an object is the reluctance of the object to change either its state of rest, or if it is moving, its motion in a straight line. In fact, this is consistent with Newton's first law of motion which can also be stated as follows: A body continues to be at rest or moving at a constant velocity unless it is acted upon by external force. In a frictional environment (like in space), it is easier to understand inertia. Consider a ball thrown in a space at a place far away from planets and other objects. The ball will continue to move in the same direction and speed until another force acts upon it. Inertia of an object is dependent on its mass. The larger the mass, the greater is its inertia. This explain why it is harder to stop moving train compared to a moving bicycle at the same speed. Below are situations which can be explained using the idea of inertia - the resistance to change in the state of rest or motion of an object. (a) When a car suddenly speeds off, its passenger is pushed back against the seat. - Intially the passenger is at rest. - When the car suddenly speeds off, the passenger tends to remain in a state of rest. - He is pushed by the seat. (b) A passenger in a fast moving car is thrown forward when the car suddenly brakes. - Intially the passenger is moving. - When the car suddenly stops, the passenger tends to continue moving because of his inertia - Hence he is thrown forward. We use a balance such as beam balance, electronic balance or sliding balance to measure mass.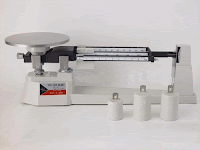 A beam balance  A sliding balance  An electronic balance |